一、前言
Android的UI开发一般采用XML代码编写和可视化编辑器(更方便)。这一部分就好比是html+css+js三剑客。
二、控件
2.1 TextView
文本框
基本属性
| 属性 |
说明 |
| layout_width |
设置控件的宽度,常用的有”wrap_content”(根据控件内容适配)、”match_parent”(与父容器同宽),以及确切数字,如200dp |
| layout_height |
设置控件的高度,同上。 |
| id |
格式为”@+id/xxx”用于在代码中获取该对象,比如java代码通过findViewById()方法获取 |
| text |
设置文字内容 |
| textColor |
设置文字颜色,格式可以为”#xxxxxxxx”,前两位代表颜色的透明度(00透明,FF不透明),后面代表RGB |
| textStyle |
设置文字风格,如normal(无效果),bold(加粗),italic(斜体) |
| textSize |
设置文字大小,单位sp |
| background |
设置控件背景颜色,”#xxxxxxxx”的格式同textColor一样,也可以是图片背景 |
| gravity |
设置控件中内容的对齐方向,如center、left、right、bottom、top等 |
| autoLink |
当文字内容出现URL,E-Mail,电话号码等,通过设置autoLink属性,可以使其成为链接,常用类别有 web、email、phone、map等 |
其中 text、textColor、background 属性的内容在开发中并不直接在控件中写明,而是写在res\values\目录下的 colors.xml、strings.xml中,然后被控件调用。例如:
1
2
3
4
5
| //在strings.xml中声明:
<string name="aaa">我被调用了</string>
//在控件中引用:
<TextView
android:text="@String/aaa"/>
|
跑马灯案例
涉及到的属性
| 属性 |
说明 |
| singleLine |
内容是否单行显示 |
| focusable |
控件是否可以获取焦点 |
| focusableInTouchMode |
用于控件在触摸模式下是否可以获取焦点 |
| ellipsize |
省略文本的模式 |
| marqueeRepeatLimit |
字母动画重复的次数 |
| clickable |
控件是否可以被点击 |
上述属性设置如下:
1
2
3
4
| android:singleLine="true"
android:ellipsize="marquee"
android:marqueeRepeatLimit="marquee_forever"
android:focusable="true"
|
实现跑马灯有以下方式:
额外设置属性值
1
2
| android:focusableInTouchMode="true"
android:clickable="true"
|
点击TextView后,获得焦点,开始跑马灯效果。
添加额外属型值
1
| android:focusableInTouchMode="true"
|
并且在同一个LinearLayout下添加
它用于请求将焦点设置到指定的元素上。
创建类继承TextView类,重写isFocused方法,使其永远返回true。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public class MyTextView extends TextView {
public MyTextView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyTextView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public MyTextView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
public boolean isFocused() {
return true;
}
}
|
按钮。Button继承于TextView,所以TextView上很多属性也可以应用到Button 上。
基本属性
| 属性 |
说明 |
| drawable |
引用的Drawable位图 |
| state_focused |
是否获得焦点 |
| state_window_focused |
是否获得窗口焦点 |
| state_enabled |
控件是否可用 |
| state_checkable |
控件可否被勾选 |
| state_checked |
控件是否被勾选 |
| state_selected |
控件是否被选择,针对有滚轮的情况 |
| state_pressed |
控件是否被按下 |
| state_active |
控件是否处于活动状态 |
| state_single |
控件包含多个子控件时,确定是否只显示一个子控件 |
| state_first、state_middle、state_last |
控件包含多个子控件时,确定哪个子控件是否处于显示状态 |
以上这些属性并不是在<button>或<android.widget.Button>下声明的,而是在\res\drawable\和\res\color\目录下创建xml文件进行声明(color这个目录自己创建,名字只能是color,因为<selector>只能在animator\,drawable\,color\下的xml文件中使用)。
按钮点击转化案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| <android.widget.Button
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:text="我是按钮"
android:textColor="#FF00FF00"
android:textSize="32dp"
android:background="@drawable/bt_image"
android:backgroundTint="@color/btn_color"
/>
|
如果使用<Button/>标签,则background和backgroundTint属性设置颜色无效!推荐使用**<android.widget.Button/>**来解决这些问题。其中background属性设置的@drawable/bt_image和backgroundTint属性设置的@color/btn_color均是自己创建的。
drawable/bt_image.xml如下:
1
2
3
4
| <selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:drawable="@drawable/baseline_airplanemode_active_24" android:state_pressed="true"/>
<item android:drawable="@drawable/baseline_airplanemode_inactive_24"/>
</selector>
|
第一<item/>设置了state_pressed="true",表示Button被点击的状态对应的图案,那么显然第二个<item/>则表示的是没有被点击状态下的图案。至于这些drawable的属性值,则是一些矢量图。
color/btn_color.xml如下
1
2
3
4
| <selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:color="@color/black" android:state_pressed="true"/>
<item android:color="#FFFF0000"/>
</selector>
|
跟drawable/bt_image.xml的解释类似,不过颜色设置的是图标的。
点击事件、长按事件、触摸事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| Button btn1 = findViewById(R.id.btn1);
btn1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Log.d(TAG, "onClick: ");;
}
});
btn1.setOnLongClickListener(new View.OnLongClickListener() {
@Override
public boolean onLongClick(View view) {
Log.d(TAG, "onLongClick: ");
return false;
}
});
btn1.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View view, MotionEvent motionEvent) {
Log.d(TAG, "onTouch: " + motionEvent.getAction());
return false;
}
});
|
长按按钮并松开(不移动),测试结果如下
1
2
3
4
| onTouch: 0
onLongClick:
onTouch: 1
onClick:
|
Touch事件触发了两次。分别是按下动作ACTION_DOWN (0)、松开动作ACTION_UP (1)。如果按住不松开并且移动,则会触发移动动作ACTION_MOVE (2)。
从上面的结果可以看出,这三个事件触发的顺序依次Touch、LongClick、Click。
在这些回调函数中,返回值为false表示不拦截点击事件消息(click动作在最后触发,没有返回值)。倘若将返回值修改为true,表示拦截点击事件消息,那么其他监听器就不会收到这个消息,因此也就不会执行相应回调函数。(从这三个事件的触发顺序是可以猜测出修改返回值后的触发情况)
onclick事件的处理函数可以在button的onClick属性处绑定。
1
2
3
4
| <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="dealClick"/>
|
1
2
3
| public void dealClick(View view) {
Toast.makeText(this, "可以的", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
|
案例
计数器,如果长按则提示信息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
btn1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Log.d(TAG, "onClick: ");
Integer cnt = Integer.parseInt(btn1.getText().toString());
cnt++;
btn1.setText(cnt.toString());
}
});
btn1.setOnLongClickListener(new View.OnLongClickListener() {
@Override
public boolean onLongClick(View view) {
Log.d(TAG, "onLongClick: ");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "请不要长按按钮", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return false;
}
});
|
2.3 EditText
输入框。EditText继承与TextView。
基本属性
| 属性 |
说明 |
| hint |
提示信息 |
| textColorHint |
提示文字的颜色 |
| inputType |
输入类型,如日期、电话、邮件等 |
| drawableLeft, drawableRight等 |
在输入框的指定位置添加图片 |
| drawablePadding |
设置图片和输入内容的间距 |
| paddingLeft, paddingRight等 |
设置内容与边框的间距 |
| selectAllOnFocus |
获得焦点后全选组件内所有文本内容 |
| minLines, maxLines |
设置最小、最大的行数,当输入内容超过最大行数,文字会自动向上滚动 |
登录案例
xml的声明如下,声明了账号框、密码框、登录按钮。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| <LinearLayout xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/zhanghao"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:inputType="text"
android:hint="请输入用户名"
android:textColorHint="#89827f"
android:drawableLeft="@drawable/baseline_account_box_24"
android:drawablePadding="20dp"
android:padding="20dp"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/mima"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:hint="请输入密码"
android:textColorHint="#89827f"
android:drawableLeft="@drawable/baseline_password_24"
android:drawablePadding="20dp"
android:padding="20dp"
/>
<android.widget.Button
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:text="登录"/>
</LinearLayout>
|
按钮设置click监听,然后获取账号密码,对比从而进行不同操作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button btn = findViewById(R.id.btn);
EditText account = findViewById(R.id.zhanghao);
EditText password = findViewById(R.id.mima);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
String ac = account.getText().toString();
String pwd = password.getText().toString();
if (ac.equals("admin") && pwd.equals("123456")){
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "管理员,欢迎你", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
else {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "账号或密码错误", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
account.setText("");
password.setText("");
}
}
});
}
|
2.4 ImageView
图片视图。
基本属性
| 属性 |
说明 |
| src |
设置图片资源 |
| scaleType |
设置图片缩放类型,如fitStart, fitCenter, fitEnd(等比缩放,位置放置不同)等 |
| maxHeight |
最大高度 |
| maxWidth |
最大宽度 |
| adjustViewBounds |
调整View的界限 |
maxHeight、maxWidth需要和adjustViewBounds一起使用,等比缩放直到一边达到最大值。
单选框。需要创建<RadioGroup>标签将多个<RadioButton>聚集为一组,确保一次只选择一个单选按钮。
要为每个RadioButton添加一个id,不然单选功能会生效!
基本属性
| 属性 |
说明 |
| checked |
默认是否勾选 |
| drawableXXX(Left, Right) |
文字与选择框的相对位置。需要与button=”@null”一起使用。 |
| paddingXxx |
文字与选择框的距离 |
| button |
设置为@null表示不使用默认的选择框 |
案例
性别选择,通过提交按钮显示你选择的性别或者在改变时提示选择的性别。
xml配置如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="请选择你的性别:"
android:textSize="24dp"/>
<RadioGroup
android:id="@+id/radiogroup"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rbtnman"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="man"
android:textSize="24dp"
android:checked="true"/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rbtnwoman"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="woman"
android:textSize="24dp"/>
</RadioGroup>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnpost"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:text="提交"
/>
|
MainActivity如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity{
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
RadioGroup rg = findViewById(R.id.radiogroup);
Button btnpost = findViewById(R.id.btnpost);
btnpost.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
for (int i = 0; i<rg.getChildCount(); i++){
RadioButton childbtn = (RadioButton) rg.getChildAt(i);
if (childbtn.isChecked()){
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "你选者了" + childbtn.getText().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
});
}
}
|
方法一是通过给RadioGroup设置CheckedChange监听,直接获取被选择的RadioButton的id,通过id找到该控件。
方法二是通过给按钮设置Click监听,遍历RadioGroup下的RadioButton,查看RadioButton是否被选择。
2.6 CheckBox
复选框。对于每一个复选框,使用<CheckBox>单独创建即可。
基本属性
属性同RadioButton。
案例
同RadioButton。
一种方法是给所有CheckBox设置CheckedChanged监听,使用isChecked()方法判断是否被选中。
1
2
3
4
| public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton compoundButton, boolean b) {
if(compoundButton.isChecked())
Toast.makeText(this,compoundButton.getText().toString(),Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
|
另一种方法是给提交按钮设置click监听,然后遍历所有CheckBox,使用isChecked()方法判断是否被选中。由于CheckBox是独立存在的,并不像RadioButton一样有父标签RadioGroup,所以不能直接使用for循环判断。
2.7 ProgressBar
进度条。
基本属性
| 属性 |
说明 |
| max |
进度条最大值 |
| progress |
进度条已经完成进度值 |
| indeterminate |
如果设置成true,则进度条不精确显示进度 |
| progressDrawable |
设置轨道对应的Drawable对象 |
| secondaryProgress |
二级进度条,类似于视频播放的一条是当前播放进度,一条是缓冲进度,前者通过progress属性进行设置 |
| style |
进度条样式 |
案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
<ProgressBar
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
/>
<ProgressBar
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
<ProgressBar
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:indeterminate="true"
/>
|
其中条形进度条设置indeterminate为true后,和圆形进度条类似,在不断地流动。
由于系统提供的比较简陋,在开发中一般都用动画(Animation)来代替或者自定义进度条(继承ProgressBar或者view)。
2.8 Notification
状态栏通知。
要想实现通知,需要获得两个对象:
NotificationMannager
NotificationManager类是一个通知管理器类,这个对象是由系统维护的服务,是以单例模式的方式获得,所以一般并不直接实例化这个对象。在Activity中,可以使用Activity.getSystemService(String)方法获取NotificationManager对象,这里传递Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE即可。
1
| NotificationManager notification_manager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
|
Notification
使用NotificationCompat类的Builder构造器来创建Notification对象,可以保证程序在所有的版本上都能正常工作。Android8.0新增了通知渠道这个概念,如果没有设置,则通知无法在Android8.0的机
器上显示。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
NotificationCompat.Builder builder = new NotificationCompat.Builder(this, "nid001");
......
Notification notification = builder.build();
|
由于通知渠道的引进,我们要创建通知渠道并与通知管理服务绑定
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O){
NotificationChannel channel = new NotificationChannel("nid001","测试通知", NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_HIGH);
notification_manager.createNotificationChannel(channel);
}
|
需要注意的是Builder创建时的参数id和Channel创建时的参数id要一致。
NotificationChannel的Importance参数如下:
| 类型 |
说明 |
| IMPORTANCE_NONE |
关闭通知 |
| IMPORTANCE_MIN |
开启通知,不会弹出,但没有提示音,状态栏中无显示 |
| IMPGRTANCE_LOW |
开启通知,不会弹出,不发出提示音,状态栏中显示 |
| IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT |
开启通知,不会弹出,发出提示音,状态栏中显示 |
| IMPORTANCE_HIGH |
开启通知,会弹出,发出提示音,状态栏中显示 |
NotificationCompat.Builder的基本方法
| 方法 |
说明 |
| setContentTitle(String string) |
设置标题 |
| setContentText(String string) |
设置文本内容 |
| setSmallIcon(int icon) |
设置小图标,只是用alpha图层,即图标不能带颜色 |
| setLargeIcon(int argb) |
设置小图标颜色 |
| setContentIntent(PendingIntent intent) |
设置点击通知后的跳转意图 |
| setAutoCancel(boolean bool) |
设置点击通知后自动清除通知 |
| setWhen(long when) |
设置通知的创建事件 |
其中前三个方法是必须的,否则程序无法正常工作。
案例
通过按钮创建和清楚通知,并且点击通知会跳转到另一个页面(activity)。
xml声明如下。通过onClick属性绑定点击事件处理方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <Button
android:layout_width="165dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:onClick="sentNotification"
android:text="发送通知" />
<Button
android:layout_width="165dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:onClick="cacelNotification"
android:text="取消通知" />
|
MainActivity方法如下。获取通知管理服务(NotificationManager),创建通信渠道(channel)并与通知管理服务绑定。创建PendingIntent设置跳转意图。创建Notification对象,最后实现点击事件处理方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG = "";
private NotificationManager notification_manager;
private Notification notification;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
notification_manager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O){
NotificationChannel channel = new NotificationChannel("nid001","测试通知",
NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_HIGH);
notification_manager.createNotificationChannel(channel);
}
Intent intent = new Intent(this, NotificationActivity.class);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_IMMUTABLE);
notification = new NotificationCompat.Builder(this,"nid001")
.setContentTitle("叶华")
.setContentText("喂喂喂")
.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.baseline_account_box_24)
.setLargeIcon(BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),R.drawable.wallhaven))
.setColor(Color.parseColor("#FFFF0000"))
.setContentIntent(pendingIntent)
.setAutoCancel(true)
.build();
}
public void sentNotification(View view){
notification_manager.notify(111,notification);
}
public void cacelNotification(View view){
notification_manager.cancel(111);
}
}
|
其中NotificationActivity方法如下。只是简单的在Logcat处输出信息:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public class NotificationActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Log.d("","点击消息进入到了NotificatoinActivity");
}
}
|
工具栏。
基本属性
| 属性 |
说明 |
| layout_width、layout_height |
宽高,layout_height一般设置为“?attr/actionBarSize” |
| background |
背景色或背景图 |
| navigationIcon |
导航图标,比如返回图标 |
| title |
标题 |
| subtitle |
子标题 |
| logo |
图标 |
案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="#00FFFF"
app:title="大标题"
app:subtitle="小标题"
app:titleMarginStart="100dp"
app:navigationIcon="@drawable/baseline_arrow_back_24"
app:logo="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
/>
|
一般标题都是居中显示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:orientation="vertical">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="#00FFFF"
app:navigationIcon="@drawable/baseline_arrow_back_24"
app:logo="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="标题"
android:layout_gravity="center"
/>
</androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar>
</LinearLayout>
|
在TextView中设置了标题就不要在<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar>里面再设置标题了。由于是androidx里面的Toolbar,与android里面的Toolbar不同,需要注意在java代码中使用该对象时不要导错包(import androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar)。
2.10 AlertDialog
对话框。
AlertDialog.Builder的基本方法
| 方法 |
说明 |
| setIcon(int iconId) |
设置图标 |
| setTitle(Charsequence title) |
添加标题 |
| setMessage(CharSequence message) |
添加消息 |
| setView(View view) |
设置自定义布局 |
| setPositiveButton |
确定按钮 |
| setNegativeButton |
取消按钮 |
| setNeutralButton |
中间按钮 |
| create() |
创建对话框 |
| show() |
显示对话框 |
案例
实现以上功能。
触发按钮的xml设置如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:text="点击显示窗口"
android:onClick="ClickWindow"
/>
|
绑定了ClickWindow方法。
MainActivity方法如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG = "";
private AlertDialog dialog;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(this);
dialog = builder.setIcon(R.drawable.baseline_account_box_24)
.setTitle("我是对话框")
.setMessage("阿巴阿巴......")
.setPositiveButton("确认", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
Log.d("","点击确认");
}
})
.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
Log.d("","点击取消");
}
})
.setNeutralButton("中立", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
Log.d("","点击中立");
}
})
.setView(R.layout.dialog_view)
.create();
}
public void ClickWindow(View view) {
dialog.show();
}
}
|
显然,首先要创建的是AlertDialog.Builder对象,然后通过一系列方法设置属性。其中setView方法的参数是自己创建的一个布局的xml文件。最后实现ClickWindow方法来处理点击事件。
悬浮框。
PopupWindow弹出后,所有的触屏和物理按键都由PopupWindows 处理。其他任何事件的响应都必须发生在PopupWindow消失之后,(home 等系统层面的事件除外)。
基本方法
| 方法 |
说明 |
| PopupWindow(View contentView, int width, int height, boolean focusable) |
多个构造方法,这里拿一个来说明。参数contentView指PopupWindow的布局,参数width和height一般设置ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,参数focusable指是否显示焦点,即点击该布局之外的地方可以退出。 |
| setContentView(View contentView) |
设置PopupWindow显示的View |
| getContentView() |
获得PopupWindow显示的View |
| showAsDropDown(View anchor) |
相对某个控件的位置(正左下方),无偏移 |
| showAsDropDown(View anchor, int xoff, int yoff) |
相对某个控件的位置,有偏移 |
| setFocusable(boolean focusable) |
设置焦点 |
| setBackgroundDrawable(Drawable background) |
设置背景 |
| setAnimationStyle(int animationStyle) |
设置动画效果 |
| dismiss() |
关闭弹窗 |
案例
xml配置如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:text="点击显示PopupWindow"
android:onClick="ClickButton"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/haha"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="哈哈哈哈哈"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/xixi"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="嘻嘻嘻嘻"/>
</LinearLayout>
|
MainActivity如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity{
private static final String TAG = "";
private PopupWindow popupWindow;
private View popupwindow_view;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
popupwindow_view = getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.popupwindow_view, null);
popupWindow = new PopupWindow(popupwindow_view,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
true);
popupWindow.setBackgroundDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.wallhaven));
Button haha = popupwindow_view.findViewById(R.id.haha);
Button xixi = popupwindow_view.findViewById(R.id.xixi);
haha.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "你点击了哈哈哈", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
popupWindow.dismiss();
}
});
xixi.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "你点击了嘻嘻嘻", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
popupWindow.dismiss();
}
});
}
public void ClickButton(View view) {
popupWindow.showAsDropDown(view);
}
}
|
2.12 ListView
列表。列表中的每一项(item)都有自己的布局。item的布局单独创建一个layout的xml文件,并对该布局创建一个类,同时也要创建对应的Adapter类,用来给item填充数据等。
什么是Adapter?
答:
Adapter(适配器)是一个用于将数据与视图进行绑定的桥梁。简单点说,就是将各种数据以合适的形式显示到view上,提供给用户看。(个人的理解是Adapter将数据从布局中分离开来)
常用的几个Adapter类
- BaseAdapter:是一个抽象类,提供了一个基本的Adapter实现,可以用于自定义Adapter的开发。
- ArrayAdapter:是BaseAdapter的子类,用于将数组或List数据绑定到ListView中。
- SimpleAdapter:是BaseAdapter的子类,用于将键值对数据绑定到ListView中的多个TextView组合的布局中。
- CursorAdapter:是BaseAdapter的子类,用于将数据库Cursor中的数据绑定到ListView中。
- RecyclerView.Adapter:用于RecyclerView组件的适配器,支持更强大的列表项定制和动画效果。
基本属性
| 属性 |
说明 |
| divider |
设置表项之间的分隔条,可以用颜色分割,也可以用drawable资源分割 |
| dividerHeight |
设置表项之间分割线的高度 |
| dividerPadding |
设置表项之间分割线的左右内边距 |
| listSelector |
设置表项被选中时的背景样式 |
| scrollbars |
设置滚动条的显示方式,如”vertical”(垂直滚动条)、”horizontal”(水平滚动条)和”none”(不显示滚动条) |
| headerDividersEnabled, footerDividersEnabled |
是否显示列表头部和尾部的分割线,默认为true |
案例
实现类似QQ的消息列表。(目的在于学会使用Adapte)
首先activity_main.xml中创建一个ListView就行了。
1
2
3
4
5
| <ListView
android:id="@+id/lv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</ListView>
|
另外创建一个xml文件用于列表中item的布局。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_width="135dp"
android:layout_height="128dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="@+id/textView3"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/textView3"
tools:srcCompat="@tools:sample/avatars" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="275dp"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:text="TextView"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView3"
android:layout_width="275dp"
android:layout_height="94dp"
android:text="TextView"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/textView2" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
|
这里使用ConstraintLayout布局很方便,只要拖拽组件,连线就可以制作好。
因为信息不存放在xml文件中,所以创建一个类来描述item。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
public class Person {
private String name;
private String text;
private int pIcon;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, String text, int pIcon) {
this.name = name;
this.text = text;
this.pIcon = pIcon;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getText() {
return text;
}
public void setText(String text) {
this.text = text;
}
public int getpIcon() {
return pIcon;
}
public void setpIcon(int pIcon) {
this.pIcon = pIcon;
}
}
|
再写个类继承BaseAdapter用来将数据显示在页面中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| public class PersonAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private ArrayList<Person> data;
private Context context;
public PersonAdapter() {
}
public PersonAdapter(ArrayList<Person> data, Context context) {
this.data = data;
this.context = context;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return data.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int i) {
return data.get(i);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int i) {
return i;
}
@Override
public View getView(int i, View view, ViewGroup viewGroup) {
ViewHolder viewHolder;
if (view == null){
view = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.item_view, viewGroup, false);
viewHolder = new ViewHolder();
viewHolder.Icon = view.findViewById(R.id.imageView);
viewHolder.Name = view.findViewById(R.id.textView2);
viewHolder.Message = view.findViewById(R.id.textView3);
view.setTag(viewHolder);
} else {
viewHolder = (ViewHolder) view.getTag();
}
Person person = data.get(i);
viewHolder.Icon.setBackgroundResource(person.getpIcon());
viewHolder.Name.setText(person.getName());
viewHolder.Message.setText(person.getText());
return view;
}
private final class ViewHolder{
ImageView Icon;
TextView Name;
TextView Message;
}
}
|
对于getView方法,有多少个item就会调用多少次getView方法,里面的inflate方法和findViewById方法会被调用多次,这是非常耗时的。
但是getView方法中的参数view是系统提供的视图缓存对象。所以通过if语句的判断view是否已经创建,就不会执行多次inflate方法。同时创建ViewHolder类存放item的组件,通过view.setTag(viewHolder)放入view中,相当于也缓存item中的控件引用,以便后续复用(比如屏幕上下滑动,同一个item多次出现、隐藏的情况)。
最后MainActivity.java如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity{
private ArrayList<Person> PersonArrayList;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
PersonArrayList = new ArrayList<Person>();
PersonArrayList.add(new Person("送之", "在吗?", R.drawable.wallhaven));
PersonArrayList.add(new Person("无阿", "Vivo50", R.drawable.wallhaven));
PersonArrayList.add(new Person("吉拉", "6", R.drawable.wallhaven));
PersonArrayList.add(new Person("阿三", "?", R.drawable.wallhaven));
PersonArrayList.add(new Person("骗子", "我是秦始皇", R.drawable.baseline_account_box_24));
ListView listviewByid = findViewById(R.id.lv);
listviewByid.setAdapter(new PersonAdapter(PersonArrayList, this));
}
}
|
2.13 RecyclerView
RecyclerView比ListView更加灵活,RecyclerView在继承RecyclerView.Adapter时会强制让我们实现ViewHolder,同时也提供了多个布局可供选择。
直接上案例。
案例
同ListView的案例。主要是继承RecyclerView.Adapter处有区别。
PersonAdapter.java如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
public class PersonAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<PersonAdapter.ViewHolder> {
private ArrayList<Person> data;
private Context context;
public PersonAdapter(ArrayList<Person> data, Context context) {
this.data = data;
this.context = context;
}
public ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View view = View.inflate(context, R.layout.item_view, null);
return new ViewHolder(view);
}
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull ViewHolder holder, int position) {
Person person = data.get(position);
holder.Icon.setBackgroundResource(person.getpIcon());
holder.Name.setText(person.getName());
holder.Message.setText(person.getText());
}
public int getItemCount() {
return data == null ? 0:data.size();
}
public class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
private ImageView Icon;
private TextView Name;
private TextView Message;
public ViewHolder(@NonNull View itemView) {
super(itemView);
Icon = itemView.findViewById(R.id.imageView);
Name = itemView.findViewById(R.id.textView2);
Message = itemView.findViewById(R.id.textView3);
}
}
}
|
看似那么多方法,但做的事情并没有变:通过inflate方法获取view,创建ViewHolder对象,通过findViewById方法获取item中的组件,通过setxxx方法设置数据。只不过是将这些工作细化为多个方法了。
MainActivity.java如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity{
private ArrayList<Person> PersonArrayList;
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
......
RecyclerView recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.rv);
PersonAdapter personAdapter = new PersonAdapter(PersonArrayList, this);
recyclerView.setAdapter(personAdapter);
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this));
}
}
|
以上基本就实现了RecyclerView。
然后再给item来个点击事件的监听和处理。
这部分主要在PersonAdapter.java中额外添加一下方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
private OnRecyclerItemOnClickListener monRecyclerItemOnClickListener;
public interface OnRecyclerItemOnClickListener{
void onRecyclerItemClick(int postion);
}
public void setRecyclerItemOnClickListener(OnRecyclerItemOnClickListener listener){
monRecyclerItemOnClickListener = listener;
}
|
同时还需要在继承了RecyclerView.ViewHolder类的ViewHolder类的ViewHolder方法中给item设置监听
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
itemView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
if (monRecyclerItemOnClickListener != null){
monRecyclerItemOnClickListener.onRecyclerItemClick(getAdapterPosition());
}
}
});
|
最后在MainActivity.java中给Adapter创建监听并实现接口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| personAdapter.setRecyclerItemOnClickListener(new PersonAdapter.OnRecyclerItemOnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onRecyclerItemClick(int postion) {
Log.d("leo", "点击了第"+postion+"个item");
}
});
|
咋一看,怎么设置了两次监听?其实在MainActivity.java的调用的setRecyclerItemOnClickListener方法实际上是为了给外部提供一个接口,让外部有机会设置自己的监听器monRecyclerItemOnClickListener来处理item的点击事件。(并不是继承View.OnClickListener重写onClick方法)
而给item设置的监听,才会在我们点击页面中的列表项时触发。
(可以尝试理解为item在页面中有对应控件,是可以点击到的,而Adapter在页面中并不没有。当然这样理解并不是很正确)
(不妨可以直接将OnRecyclerItemOnClickListener接口写成方法试试,但一般不将处理函数写死)
ViewPager是一个页面切换组件,常用于创建轮播图、图片浏览、导航页面等需要左右滑动切换内容的场景。使用<androidx.viewpager.widget.ViewPager>或者<androidx.viewpager2.widget.ViewPager2>标签。需要PagerAdapter创建Adapter对象与ViewPager对象绑定。
在开发中经常与Fragment搭配使用,官方给我们提供了两个专门用于Fragment的Adapter:FragmentPageAdapter和FragmentStatePagerAdapter:
- FragmentPageAdapter:和PagerAdapter一样,只会缓存当前的Fragment以及左边一个,右边 一个,即总共会缓存3个Fragment。
- FragmentStatePagerAdapter:当Fragment对用户不可见时,整个Fragment会被销毁, 只会保存Fragment的状态。而在页面需要重新显示的时候,会生成新的页面。
(与viewpager2搭配使用!)
基本方法
| 方法 |
说明 |
| instantiateItem() |
①将给定位置的view添加到ViewGroup(容器)中,创建并显示出来
②返回一个代表新增页面的Object(key),通常都是直接返回view本身就可以了,当然你也可以自定义自己的key,但是key和每个view要一一对应的关系 |
| isViewFromObject() |
判断instantiateItem函数所返回来的Key与一个页面视图是否是代表的同一个视图(即它俩是否是对应的,对应的表示同一个View),通常我们直接写 return view == object |
| destroyItem() |
从ViewGroup容器中移除对应位置的视图对象,即摧毁对应页面视图 |
| getPageTitle() |
获取指定位置页面的标题 |
案例
页面切换。
先随便在layout文件夹下创建三个布局。
然后创建一个继承PagerAdapter的类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public class ViewAdapter extends PagerAdapter {
private List<View> viewList;
public ViewAdapter(List<View> viewList) {
this.viewList = viewList;
}
public int getCount() {
return viewList == null? 0 : viewList.size();
}
public boolean isViewFromObject(@NonNull View view, @NonNull Object object) {
return view == object;
}
public Object instantiateItem(@NonNull ViewGroup container, int position) {
container.addView(viewList.get(position), 0);
return viewList.get(position);
}
public void destroyItem(@NonNull ViewGroup container, int position, @NonNull Object object) {
container.removeView(viewList.get(position));
}
}
|
MainActivity.java如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity{
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
LayoutInflater inflater = getLayoutInflater().from(this);
View vp1 = inflater.inflate(R.layout.viewpage1,null);
View vp2 = inflater.inflate(R.layout.viewpage2,null);
View vp3 = inflater.inflate(R.layout.viewpage3,null);
List<View> viewList = new ArrayList<>();
viewList.add(vp1);
viewList.add(vp2);
viewList.add(vp3);
ViewPager viewPager = findViewById(R.id.vp);
ViewAdapter viewAdapter = new ViewAdapter(viewList);
viewPager.setAdapter(viewAdapter);
}
}
|
三、布局
也就是放置控件、布局的容器,可以多层嵌套。
布局中的所有元素均使用 View 和 ViewGroup 对象的层次结构进行构建。View 通常用于绘制用户可看到并与之交互的内容。ViewGroup 则是不可见的容器。
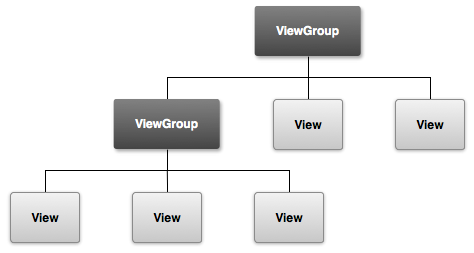
View 对象通常称为“微件”,可以是多个子类之一,例如 Button 或 TextView。ViewGroup 对象通常称为“布局”,可以是提供不同布局结构的众多类型之一,例如 LinearLayout 或 ConstraintLayout。
3.1 LinearLayout
线性布局
基本属性
| 属性 |
说明 |
| orientation |
布局中组件的排列方式,如horizontal(水平摆放)、vertical(垂直拜访,即一个控件占一整行) |
| gravity |
控制组件或布局所包含的子元素的对齐方式,可以多个组合,以 | 分隔,如 bottom|left表示位置在左下方 |
| layout_gravity |
控制当前组件在父容器的对齐方式 |
| background |
为当前组件设置背景(图片、颜色) |
| divider |
分割线。与showDividers搭配使用 |
| showDividers |
设置分割线所在的位置,如none(无)、beginning(开始)、end(结束)、middle(每两个组件间) |
| dividerPadding |
设置分隔线与左右两边的间距 |
| layout_weight |
等比例划分剩余区域 |
案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
| <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center"
android:background="@drawable/wallhaven"
android:divider="@drawable/baseline_password_24"
android:showDividers="middle"
android:dividerPadding="100dp"
>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:gravity="center">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="LinearLayout嵌套LinearLayout"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="请选择你喜欢吃的水果:"
android:layout_gravity="left"
android:textSize="24dp"/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/apple"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="苹果"
android:textSize="24dp"
android:layout_gravity="right"
/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/banana"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="香蕉"
android:textSize="24dp"
/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/pear"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="梨"
android:textSize="24dp"
/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/Cantaloupe"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="哈密瓜"
android:textSize="24dp"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnpost"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:text="提交"
android:onClick="postByclick"
/>
</LinearLayout>
|
3.2 RelativeLayout
相对布局。
基本属性
| 属性 |
说明 |
| gravity |
控制组件或布局所包含的子元素的对齐方式 |
| ignoreGravity |
设置为true将不受gravity属性的影响 |
| layout_alignParentXXXX(Left, Right等) |
根据父容器定位。左(右)对齐 |
| layout_centerXXXX(Horizontal, Vertical, InParent) |
根据父容器定位。水平居中,垂直居中,中间位置 |
| layout_XXX(toLeftOf, toRightOf, above, below, alignTop, alignBottom, alignLeft, alignRight) |
根据兄弟组件定位。根据id来设置。其中toLeftOf, toRightOf, above, below是参考组件的左、右、上、下边,而alignTop, alignBottom, alignLeft, alignRight则是对齐参考组件的上、下、左、右边界。 |
| layout_XXX(margin, marginLeft, marginRight, marginTop, marginBottom) |
设置组件与父容器的边距(偏移) |
| padding, paddingXXX(Left, Right, Top, Bottom) |
设置组件内部元素间的边距 |
案例
实现梅花布局。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| <RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_center"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_left"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/btn_center"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_right"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/btn_center"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_top"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_above="@id/btn_center"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_bottom"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_below="@id/btn_center"
android:layout_centerInParent="true" />
</RelativeLayout>
|
3.3 FrameLayout
帧布局。从父容器左上角开始绘制,按组件或布局的定义顺序依次绘制,造成覆盖效果。
基本属性
| 属性 |
说明 |
| foreground |
设置前景图像 |
| foregroundGravity |
设置前景图像显示的位置 |
案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| <FrameLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
>
<android.widget.Button
android:layout_width="400dp"
android:layout_height="400dp"
android:background="#FFFF0000"
/>
<android.widget.Button
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#FF00FF00"
/>
<android.widget.Button
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:background="#FF0000FF"
/>
<android.widget.Button
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#FFFFFF00"
android:foreground="@drawable/baseline_airplanemode_active_24"
android:foregroundGravity="center"
/>
</FrameLayout>
|
3.4 TableLayout
表格布局。
<TableLayout>表格标签,内嵌<TableRow>表行标签
基本属性
| 属性 |
说明 |
| collapseColumns |
设置需要被隐藏的列的序号,序号从0开始。可以设置多个,用逗号隔开,比如”0,2”,如果是所有列都生效,则用”*“号即可 |
| stretchColumns |
设置允许被拉伸的列的列序号,序号从0开始。设置同上。只要存在一行是满的,设置就对所有行无效。无法控制被拉伸的控件的长度 |
| shrinkColumns |
设置允许被收缩的列的列序号,序号从0开始。设置同上。只要存在一行有空隙,设置就对所有行无效。无法控制被收缩的控件的长度 |
| layout_column |
设置子控件显示在第几列 |
| layout_span |
设置子控件横向跨几列 |
3.5 GridLayout
网格布局。
与TableLayout有点类似,但比它更好用,功能(属性)更多。
基本属性
| 属性 |
说明 |
| orientation |
设置水平显示还是垂直显示 |
| columnCount |
设置行的显示个数。 |
| rowCount |
设置列的显示个数。 |
| layout_row, layout_column |
设置子控件显示在第几行第几列。从0开始,可以覆盖。后面没有定义行列的控件会跟随当前控件移动。 |
| layout_rowSpan, layout_columnSpan |
设置子控件横跨几行几列。需要设置android:layout_gravity = “fill”才能生效 |
| layout_gravity |
设置子控件在网格中的显示位置,如left, right等 |
| layout_columnWeight, layout_rowWeight |
设置子控件的横向(或纵向)剩余空间的分配权重。与LinearLayout布局的属性layout_weight相同 |
案例
实现计算器布局。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| <GridLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:columnCount="4"
android:rowCount="7"
>
<TextView
android:text="9+1"
android:textSize="24sp"
android:background="#fecccb"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_gravity="fill"
android:layout_columnSpan="4"
/>
<android.widget.Button
android:text="回退"
android:layout_columnSpan="2"
android:layout_gravity="fill"
/>
<android.widget.Button
android:text="归零"
android:layout_columnSpan="2"
android:layout_gravity="fill"
/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="7"/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="8"/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="9"/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="+"/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="4"/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="5"/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="6"/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="-"/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="1"/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="2"/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="3"/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="*"/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="0"/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="."/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="="/>
<android.widget.Button android:text="/"/>
</GridLayout>
|
3.6 ConstraintLayout
约束布局。
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>标签。
可以在Design模式下,拖动控件进行布局,更加方便,进行可视化布局,Infer Constraints功能可以直接帮你设置好约束(比如距离控件或父容器的各种设置),当然也可以在Attributes处进行更详细的设置。
四、动画
4.1 逐帧动画
把多张图片快速播放形成的动画。
使用方法:
<animation-list>作为大标签,内部设置多个<item>小标签(对应多张图片),<item>标签设置图片资源(drawable)和图片显示的时间(duration)。
基本属性
| 属性 |
说明 |
| drawable |
图片资源 |
| duration |
图片显示的时间,单位为ms。每张图片显示的时间可以单独设置 |
基本方法
| 方法 |
说明 |
| start() |
播放动画 |
| stop() |
停止动画 |
案例
动画xml如下
1
2
3
4
5
| <animation-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:drawable="@drawable/baseline_airplanemode_active_24" android:duration="120"/>
<item android:drawable="@drawable/baseline_airplanemode_inactive_24" android:duration="120"/>
<item android:drawable="@drawable/wallhaven" android:duration="120"/>
</animation-list>
|
然后在activity_main.xml中引用。
但是并不会播放,需要通过调用start()方法来播放动画。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity{
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
LinearLayout linearlayout = findViewById(R.id.ll);
AnimationDrawable animation = (AnimationDrawable)linearlayout.getBackground();
animation.start();
}
}
|
4.2 补间动画
在指定的时间段内,通过不断地改变视图的属性值(如位置、尺寸、旋转角度、透明度等),来实现视图的平滑动画效果。
主要有以下几种类型的补间动画:
- 位移动画(Translate Animation):通过改变视图的位置实现移动效果。
- 缩放动画(Scale Animation):通过改变视图的尺寸实现缩放效果。
- 旋转动画(Rotate Animation):通过改变视图的旋转角度实现旋转效果。
- 透明度动画(Alpha Animation):通过改变视图的透明度实现淡入淡出效果。
基本属性
位移动画
| 属性 |
说明 |
| fromXDelta, fromYDelta |
起始X、Y轴位置的偏移量 |
| toXDelta, toYDelta |
结束X、Y轴位置的偏移量 |
| duration |
动画时长 |
缩放动画
| 属性 |
说明 |
| fromXScale, fromYScale |
起始X、Y轴上的缩放比例 |
| toXScale, toYScale |
结束X、Y轴上的缩放比例 |
| pivotX, pivotY |
缩放中心点的X、Y轴坐标(被缩放的控件的左上角为0%,中心为50%) |
| duration |
动画时长 |
旋转动画
| 属性 |
说明 |
| fromDegrees |
起始角度(0~360) |
| toDegrees |
结束角度 |
| pivotX, pivotY |
旋转中心点的X、Y轴坐标 |
| duration |
动画时长 |
透明度动画
| 属性 |
说明 |
| fromAlpha |
起始透明度(0.0表示完全透明,1.0表示完全不透明) |
| toAlpha |
结束透明度 |
| duration |
动画时长 |
基本方法
| 方法 |
说明 |
| start() |
开始执行动画 |
| setRepeatMode(int repeatMode) |
设置动画的重复模式 |
| setRepeatCount(int repeatCount) |
设置动画的重复次数 |
| setFillEnabled(boolean fillEnabled) |
设置是否保持动画结束时的状态 |
| setDuration(int duration) |
设置动画的持续时间,单位为毫秒 |
| setInterpolator(Interpolator interpolator) |
设置动画的插值器 |
案例
动画xml文件如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| <set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<alpha
android:fromAlpha="0"
android:toAlpha="1"
android:duration="2000"/>
<rotate
android:fromDegrees="0"
android:toDegrees="360"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:duration="2000"/>
<scale
android:fromXScale="0"
android:fromYScale="0"
android:toXScale="1"
android:toYScale="1"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:duration="2000"
/>
<translate
android:fromXDelta="0"
android:fromYDelta="0"
android:toXDelta="400"
android:toYDelta="400"
android:duration="2000"
/>
</set>
|
加载并启动该动画
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
ImageView imageview = findViewById(R.id.imageV);
Animation animation = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this, R.anim.bujian);
imageview.startAnimation(animation);
|
4.3 属性动画
属性动画(Property Animation)是一种可以改变任意对象的属性值,并实现平滑动画效果的机制。这个过程是通过插值器和估值器来计算中间属性值的。插值器控制动画的时间进度,估值器则根据时间进度计算出中间的属性值。
基本方法
| 方法 |
说明 |
| ObjectAnimator.ofXXX(target, propertyName, values, …) |
创建一个针对指定目标对象、属性名和起始值/结束值的属性动画 |
其他方法同补间动画的方法一样。
案例
两种方法设置透明度
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
TextView textView = findViewById(R.id.tv);
ValueAnimator valueAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0f, 1f);
valueAnimator.setDuration(4000);
valueAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(@NonNull ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
float animatedValue = (float) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();
Log.d("leo", "onAnimationUpdate: " + animatedValue);
textView.setAlpha(animatedValue);
}
});
valueAnimator.start();
}
|
